Expandable Co-polymer STMMA and STMMA-FD
Release Time:
2025-04-14
Expandable Co-polymer STMMA and STMMA-FD
(The lost foam casting foam-pattern-making raw material)
SPECIFICATIONS OF STMMA FOR LOST FOAM CASTING Chemical Hazard Class 9/ UN2211 American Patent: US 6770 681 B2 | |||||||
| Product | Volatile level | Moisture | Beads size | Density suggest | Suitable for castings with a minimum thickness of* | Blowing agent* | Typical Applications* |
| Name | (by wt.) | distribution peak(MM) | |||||
| STMMA#1 | ≥ 7.0% | ≦0.5% | 0.85-0.90 | 18-20g/L | 9.0mm | pentane | Ductile iron, carbon steel, and gray iron castings have hydraulic test requirements. |
| STMMA#2 | 0.65-0.85 | 19-21g/L | 8.0mm | ||||
| STMMA#3A | 0.50-0.65 | 20-22g/L | 6.0mm | ||||
| STMMA#3 | 0.36-0.50 | 21-23g/L | 5.5mm | ||||
| StMMA-FD#S | ≥ 5.5% | ≦0.5% | 0.90-1.25 | 17-19g/L | 9.0mm | pentane | Grey iron, Aluminum |
| StMMA-FD1B | 0.71-0.90 | 18-20g/L | 7.5mm | ||||
| StMMA-FD1M | 0.60-0.71 | 18-20g/L | 6.5mm | ||||
| StMMA-FD2 | 0.45-0.60 | 19-21g/L | 5.5mm | ||||
| StMMA-FD3 | 0.35-0.45 | 21-23g/L | 4.5mm | ||||
| * Density is a function of utilities and expander capabilities; the above values represent optimum expansion conditions. | |||||||
| *The selection of bead size shall be according to the minimum thickness of the casting wall, used to be 1/10 of it. If the casting needs a high precision, it can also choose the next small class. | |||||||
*Contains an additive that quickly reduces the molecular weight of polystyrene at elevated temperatures. Formula Solutions: 1.) STMMA series is focused on carbon rising defects in castings with fewer residues, low dissolution temperature. 2.) The STMMA-FD series have great advantages in solving fold defects by aluminum casting and applications in iron castings to solve excessive lustrous carbon and porosity defects etc., | |||||||
| *Typical Application means we have tested in this kind of metal, metals beyond that are according to be actually used. | |||||||
The Importance:
In the lost foam casting process, the foam pattern is very important. Choosing the suitable raw material for your foam pattern will decide the quality of your final castings.
We specially produce STMMA co-polymer resin beads for pattern making in lost foam casting, it has the below advantages compared with EPS:
- Reduces carbon defects in castings,
- Reduces lustrous carbon defects on the surface of steel/ductile iron castings
- Reduces smoke carbon and improves the surface finish of castings, to save the whole production costs.
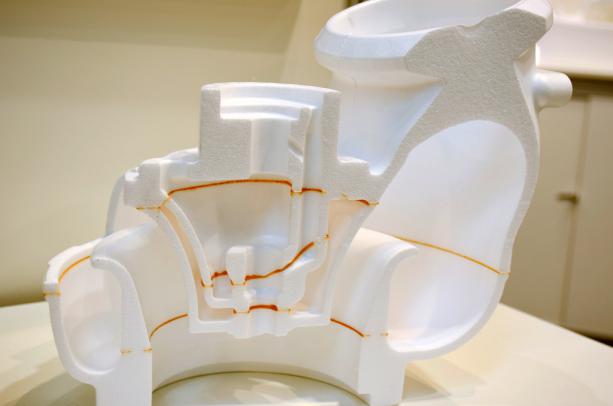
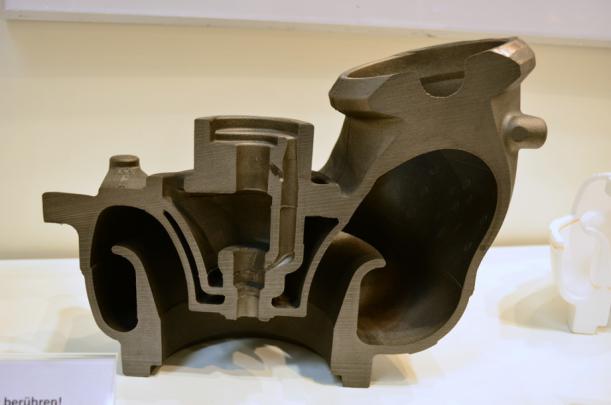


*Notes: The above collector housing is made of STMMA by our customer in Europe.
The Advantages of Using the STMMA in Lost Foam Casting:
Decomposition and gasification chemical formula when pouring metal melt:
EPS: C8H8=8C+4H2
STMMA: C5O4H8=3C+2CO2+4H2
- The carbon content of STMMA is 62%, but the carbon content in EPS is up to 93%. STMMA will greatly reduce the lustrous carbon defects in the castings.
- STMMA has a low pouring temperature, and gasification temperature generally 50℃ lower than EPS. This will help the foundry to save energy consumption in $50 to $100 per ton of castings.
- The molecular bonds are broken orderly when STMMA gasifies, accompanied by liquid low molecular residues. EPS molecules are disorderly broken, accompanied by tar-similar residues.
- The high molecular weight of STMMA will reduce the pattern's dimensional shrinkage rate. Compared with the 220 thousand molecular weights, EPS has only 50 to 60 thousand molecular weights.


The residue content after degradation of the foam pattern:
| Item | Weight of pattern | Weight of residues | Percent of Residues | Density of pattern |
| EPS | 3.37g | 2.22g | 65.90% | 21g/L |
| STMMA-FD | 3.37g | 1.03g | 30.60% | 19g/L |
| STMMA | 3.37g | 0.15g | 4.45% | 20g/L |
General Comparison:
| EPS | STMMA-FD | STMMA | |
| Molecular formula | (C8H8)n | -(C5O4H8)-m | |
| Carbon content | 92% | 82% | 63% |
| Raw beads pre-expansion temperature | 85~95 ℃ | 85~95 ℃ | 95~105 ℃ |
| Temperature of decomposition | 912℃ | 900℃ | 700℃ |
| Gas evolution of 900℃ | 600ml/g | 700ml/g | 900ml/g |
| Tapping temperature | 1500~1520℃ | 1500~1520℃ | 1450~1470℃ |
| End pouring temperature | >1470℃ | >1470℃ | >1420℃ |
| Shrinkages of pattern dimension | 0.3~0.8% | 0.3~0.8% | 0.1~0.3% |
*Notes: We suggest you don’t need to consider STMMA shrinkages when the pattern dimension is less than 300mm.
The molding process of STMMA:
| Pre-foaming | Select beads | Select type of beads based on material and quality requirement of the casting, and select the size of beads based on the minimum wall thickness of casting. |
| ▼ | ||
| Control density of pre-foamed beads | In order to give mold enough strength and rigidity, the resin beads to cast thin-wall pieces shall be controlled at density between 24~26g/L. Thick-wall pieces shall be made with large beads, with a density between 19~22g/L | |
| ▼ | ||
| Expansion of beads | Pre-heat temperature between 90~95℃, expansion temperature between 95~105℃, expansion time between 30~60s | |
| ▼ | ||
| Aging | Aging of beads | The aging time depends on the environment temperature, humidity, moisture content, and density of resin beads. Aging is an important step for achieving a quality mold |
| ▼ | ||
| Pattern-marking | Preheating of molds | The purpose of preheating mold is to shorted the forming time and reduce condensed water in cavities during molding |
| ▼ | ||
| Filling of molds | Fill with suction method, press method or both. | |
| ▼ | ||
| Heating(foam shaping) | The pressure shall be controlled between 0.2-0.3Mpa for heating steam. Pressure to be controlled between 0.11-0.14Mpa for autoclave forming, 0.10-0.12Mpa for the air chamber of the mold | |
| ▼ | ||
| Cooling | Cooling to form mold and give its strength and rigidity. Notes: cooling uniform and enough | |
| ▼ | ||
| Removing of molds | Shall prevent pattern surface from damage and deformation | |
| ▼ | ||
| Drying and stabilizing molds | Could be natural drying or drying in a ventilated room with a temperature controlled at 40-60℃, it must prevent the pattern from deformation. After drying, the moisture should be less than 1.0% |